AWS DeepRacer simulation: Car control
Roadmap
- Setup
- Launch race track in Gazebo
- Car model
- Car control
- Teleoperation
Controllers
Differential drive controller
The most popular and easiest to implement controller. Transforms angular velocity w and linear velocity v to wheel velocities vl and vr. Ideal for small robots and robot vacuums.
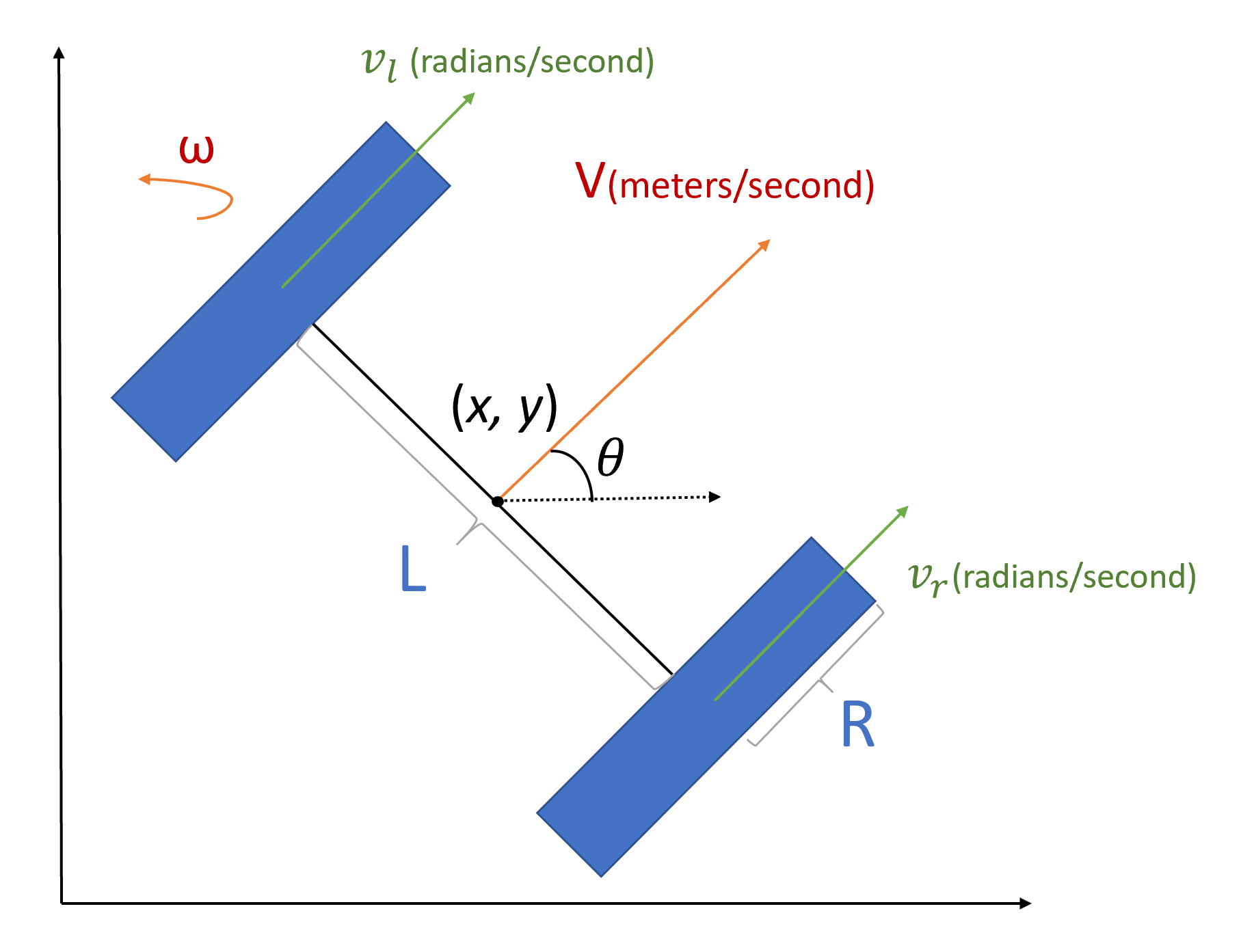
It already has implementation in ROS1 and Gazebo, you just need to add libdiffdrive_plugin.so, set distance between wheels, wheel radius, what URDF joints to use, etc. Then send v and w through cmd_vel topic and that’s pretty much all.
But….. Our car model has six continuous joints instead of two:
- left steering hinge joint
- right steering hinge joint
- front left wheel joint
- front right wheel joint
- rear left wheel joint
- rear right wheel joint
Ackermann steering drive controller
This controller is good for bicycles and cars. It should transform speed s and steering angle of the virtual center wheel φ, like on a tricycle, to two steering and two wheel commands.
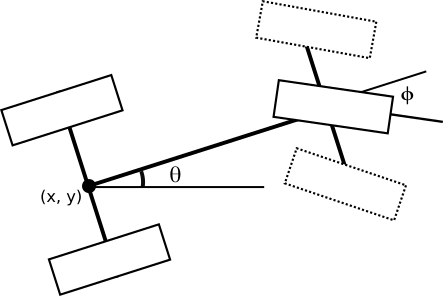
ROS1 has an implementation of this controller, but it:
- uses
cmd_veltopic withTwistmessage instead ofAckermannDrive - doesn’t work good with more than two wheels
So we will implement our version of this controller. A good tutorial shows us how simulating a robot’s controllers in Gazebo can be accomplished using ros_control and a simple Gazebo plugin adapter.
Add car control step by step with ros_controls
Add transmission elements to a URDF as macros. The most important part is hardwareInterface. Read more about transmission and hardware interfaces.
<!-- deep_ws/src/deepracer_car/urdf/xacro/macro/macros.xacro -->
<xacro:macro name="wheel_transmission" params="name">
<transmission name="${name}_transmission" type="SimpleTransmission">
<type>transmission_interface/SimpleTransmission</type>
<joint name="${name}_joint">
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/VelocityJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
</joint>
<actuator name="${name}_motor">
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/VelocityJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
<mechanicalReduction>1</mechanicalReduction>
</actuator>
</transmission>
</xacro:macro>
<xacro:macro name="steering_hinge_transmission" params="name">
<transmission name="${name}_transmission" type="SimpleTransmission">
<type>transmission_interface/SimpleTransmission</type>
<joint name="${name}_joint">
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/PositionJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
</joint>
<actuator name="${name}_motor">
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/PositionJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
<mechanicalReduction>1</mechanicalReduction>
</actuator>
</transmission>
</xacro:macro>Add the gazebo_ros_control plugin that actually parses the transmission tags and loads the appropriate hardware interfaces and controller manager
<!-- deep_ws/src/deepracer_car/urdf/xacro/control/deepracer_ros_control.xacro -->
<gazebo>
<plugin name="gazebo_ros_control" filename="libgazebo_ros_control.so">
<robotNamespace>/</robotNamespace>
<robotSimType>gazebo_ros_control/DefaultRobotHWSim</robotSimType>
<legacyModeNS>true</legacyModeNS>
</plugin>
</gazebo>Create a deep_ws/src/deepracer_car/config/racecar_control.yaml config file
# Publish all joint states -----------------------------------
joint_state_controller:
type: joint_state_controller/JointStateController
publish_rate: 60
# add four wheel controllers
left_rear_wheel_velocity_controller:
type: velocity_controllers/JointVelocityController
joint: left_rear_wheel_joint
pid: {p: 1.0, i: 0.0, d: 0.0, i_clamp: 0.0}
# add two steering controllers
right_steering_hinge_position_controller:
type: position_controllers/JointPositionController
joint: right_steering_hinge_joint
pid: {p: 1.0, i: 0.0, d: 0.5}Also add PID gains for gazebo_ros_control in that same config file
gazebo_ros_control/pid_gains:
left_rear_wheel_joint: {p: 0.1, i: 0.0, d: 0.0, i_clamp: 0.0}
right_rear_wheel_joint: {p: 0.1, i: 0.0, d: 0.0, i_clamp: 0.0}
left_front_wheel_joint: {p: 0.1, i: 0.0, d: 0.0, i_clamp: 0.0}
right_front_wheel_joint: {p: 0.1, i: 0.0, d: 0.0, i_clamp: 0.0}
left_steering_hinge_joint: {p: 0.05, i: 0.0, d: 0.0}
right_steering_hinge_joint: {p: 0.05, i: 0.0, d: 0.0}And finally create a racecar_control.launch file
<!-- deep_ws/src/deepracer_car/launch/racecar_control.launch -->
<?xml version='1.0'?>
<launch>
<!-- Load joint controller configurations from YAML file to parameter server -->
<rosparam file="$(find deepracer_car)/config/racecar_control.yaml" command="load"/>
<!-- convert joint states to TF transforms for rviz, etc -->
<node name="robot_state_publisher" pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="robot_state_publisher" output="screen"/>
<!-- The controller_spawner node starts controllers by running a python script that makes a service call to the ros_control controller manager. The service calls tell the controller manager which controllers you want. It also loads a controller that publishes the joint states of all the joints with hardware_interfaces and advertises the topic on /joint_states. The spawner is just a helper script for use with roslaunch. -->
<node name="controller_manager" pkg="controller_manager" type="spawner" respawn="false"
output="screen" args="left_rear_wheel_velocity_controller
right_rear_wheel_velocity_controller
left_front_wheel_velocity_controller
right_front_wheel_velocity_controller
left_steering_hinge_position_controller
right_steering_hinge_position_controller
joint_state_controller"/>
</launch>Fantastic. Now include this file to racecar.launch
<!-- deep_ws/src/deepracer_car/launch/racecar.launch -->
<include file="$(find deepracer_car)/launch/racecar_control.launch"/>and we can start simulation with control
roslaunch simulation simulation.launchand even send commands to each joint
rostopic pub -1 /left_rear_wheel_velocity_controller/command std_msgs/Float64 "data: 1.5"So far, so good. But do we really need to send 6 commands to control a car?
Control node
Lets add a node for more convinient control. Create a control_deepracer_car.py in a deep_ws/src/deepracer_car/scripts folder. Make a CarController with six command publishers and one AckermannDriveStamped subscriber
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import rospy
from ackermann_msgs.msg import AckermannDriveStamped
from std_msgs.msg import Float64MultiArray, Float64
from collections import OrderedDict
import math
import threading
class CarController():
def __init__(self):
self.max_speed = rospy.get_param("~max_speed", 4.0)
self.max_steering_angle = rospy.get_param("~max_steering_angle", 0.523599)
self._wheel_radius = rospy.get_param("~wheel_radius", 0.03)
self._wheel_separation = rospy.get_param("~wheel_separation", 0.159202)
self._wheel_base = rospy.get_param("~wheel_base", 0.164023)
self.update_rate = rospy.get_param("~update_rate", 50) # Hz
self._cmd_lock = threading.Lock()
# Car speed (m/s)
self.speed = 0
# Steering angle (rad)
self.steering_angle = 0
# Zero steering angle velocity means change
# the steering angle as quickly as possible.
self.steering_angle_velocity = 0
# Create publishers for controlling the car
self._velocity_pub_dict_ = OrderedDict()
self._steering_pub_dict_ = OrderedDict()
# 4 wheel publishers
self._velocity_pub_dict_["l_rear_wheel"] = rospy.Publisher('/left_rear_wheel_velocity_controller/command', Float64, queue_size=1)
self._velocity_pub_dict_["r_rear_wheel"] = rospy.Publisher('/right_rear_wheel_velocity_controller/command', Float64, queue_size=1)
self._velocity_pub_dict_["l_front_wheel"] = rospy.Publisher('/left_front_wheel_velocity_controller/command', Float64, queue_size=1)
self._velocity_pub_dict_["r_front_wheel"] = rospy.Publisher('/right_front_wheel_velocity_controller/command', Float64, queue_size=1)
# 2 steering publishers
self._steering_pub_dict_['left'] = rospy.Publisher('/left_steering_hinge_position_controller/command', Float64, queue_size=1)
self._steering_pub_dict_['right'] = rospy.Publisher('/right_steering_hinge_position_controller/command', Float64, queue_size=1)
self.cmd_sub = rospy.Subscriber("/ackermann_cmd", AckermannDriveStamped,
self.ackermann_cmd_cb, queue_size=1)
self.control()
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
rospy.init_node('control_deepracer_car', anonymous=True, log_level=rospy.INFO)
node = CarController()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Shutting down ROS control_deepracer_car node")Subscriber will update current speed and angle from ackermann_cmd topic
def ackermann_cmd_cb(self, msg):
with self._cmd_lock:
self.speed = msg.drive.speed
self.steering_angle = msg.drive.steering_angle
self.steering_angle_velocity = msg.drive.steering_angle_velocityControl will spin the node with a set rate
def control(self):
rate = rospy.Rate(self.update_rate)
update_period = 1/self.update_rate
last_time = rospy.get_time()
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
t = rospy.get_time()
delta_t = t - last_time
if delta_t>=update_period:
# Calculate target velocity and position values and publish the commands
with self._cmd_lock:
t_speed, t_left_steering, t_right_steering = self.calc_target_speed_steering(delta_t)
self.publish_commands(t_speed, t_left_steering, t_right_steering)
last_time = t
rate.sleep()will also calculate target speed and steering, ignore numbers out of bounds stabilize a stopped car
def calc_target_speed_steering(self, delta_t):
# don't go backwards for speed < 0
target_speed = max(min(self.max_speed, self.speed), 0)
target_steer_angle = max(min(self.max_steering_angle, self.steering_angle), -self.max_steering_angle)
tanSteer = math.tan(target_steer_angle)
t_left_steering = math.atan2(tanSteer, 1.0 - self._wheel_separation / 2.0 / self._wheel_base * tanSteer)
t_right_steering = math.atan2(tanSteer, 1.0 + self._wheel_separation / 2.0 / self._wheel_base * tanSteer)
t_speed = target_speed / self._wheel_radius
if self.steering_angle_velocity == 0:
t_left_steering = t_right_steering = target_steer_angle
# when speed==0 center wheels, else a car will spin
if t_speed==0:
t_left_steering = t_right_steering = 0
return t_speed, t_left_steering, t_right_steeringand will finally publish wheel and steering commands to the corresponding command topics
def publish_commands(self, t_speed, t_left_steering, t_right_steering):
'''Publishes the given action to all the topics in the given dicts
velocity_pub_dict - Dictionary containing all the velocity joints
steering_pub_dict - Dictionary containing all the movable joints
t_left_steering, t_right_steering - Desired amount, in radians, to move the movable joints by
t_speed - Angular velocity which the velocity joints should rotate with
'''
for _, pub in self._velocity_pub_dict_.items():
pub.publish(t_speed)
self._steering_pub_dict_['left'].publish(t_left_steering)
self._steering_pub_dict_['right'].publish(t_right_steering)